The console at the bottom of the MGOB interface allows a user to select:

- Which genomes to display by selecting and unselecting them.
- What version of MGOB to use.
- What window size to display. This varies from ±4 genes up to ±50. The larger the window size the longer the browser will take to display the information.
- Which gene to focus the display on.
- Whether to turn non-protein coding NPC features (tRNA genes, centromeres etc.) on or off.
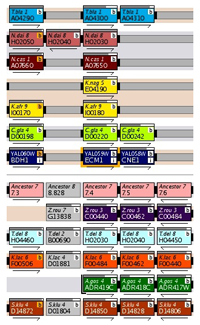 Gene Name Box
Gene Name BoxIn MGOB genes are represented by boxes featuring gene and chromosome information. Each genome has a colour pallette (red, green, blue etc.) which is used to distinguish genes from different chromosomes or contigs - genes without synteny are coloured grey.
Additional features are displayed on screen as well. Centromeres are displayed by black boxes and RNA features (e.g. tRNA genes) are shown by white boxes.
In-Focus Gene
The gene in focus is highlighted by a orange border. A user can click on any other gene to refocus MGOB on it.
Arrows
The arrows under each gene box denote the gene's relative transcriptional orientation.
'Length' Bars
Bars at the top of gene boxes that show the relative length of homologs, normally coloured grey, they are coloured salmon if the gene contains an intron. Rolling over the bar gives the exact percentage and length.
Connectors join nearby genes - a solid connector for adjacent genes, two small bars for genes within 5 genes of each other and one small bar if they are within 20 genes. These connectors are usually coloured black, but are highlighted in orange if they denote an inversion. The connectors are continued over any intervening space between genes with grey extensions.
Clicking on solid connectors or their grey extensions (i.e. connectors between adjacent genes in a genome) links to the intergenic sequence between those two genes.
Banding
Alternating grey and salmon bands behind the tracks in MGOB link genomes from the same evolutionary clade.
Brackets
The end of a chromosome or contig is denoted by a bracket around the gene's box.
Genes that we have annotated ourselves in MGOB. These are all of the form '[Genome Short Code]_MGOB_[Gene Name]' and so are easily recognised.
Curators have the ability to turn off annotated but dubious features, these however remain in the annotation files (flagged with 'OFF') in case users are interested in them. In addition, clicking through to an intergenic region containing such a feature will display a note of its existence.
 Each gene box has a "b" button which when clicked opens a window with BLAST (blastp) results for that gene against the yeast genomes in the browser. Results are highlighted in red if they are in the same column as the gene, blue if they appear on
screen outside of its column, and orange if they are a tandem copy of the gene.
Normally coloured white, the "b" button is orange when the gene has a tandem repeat on screen nearby.
Each gene box has a "b" button which when clicked opens a window with BLAST (blastp) results for that gene against the yeast genomes in the browser. Results are highlighted in red if they are in the same column as the gene, blue if they appear on
screen outside of its column, and orange if they are a tandem copy of the gene.
Normally coloured white, the "b" button is orange when the gene has a tandem repeat on screen nearby.
The first three columns after the hit's gene name shows the gene's species shortcode, the hit's ancestral pillar, if any and the ON/OFF status of the hit. Hits from genomes not selected for display are listed in italic. Users can also now select some or all of the listed hits for processing by MGOB's various bioinformatics tools.
Extracts the protein sequences for genes in a column.
"nt" Button
Extracts the nucleotide sequences for genes in a column.
"msa" Button
 Outputs a MUSCLE multiple sequence alignment of the the protein sequences of the genes in a column.
Outputs a MUSCLE multiple sequence alignment of the the protein sequences of the genes in a column.
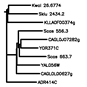
"tree" Button
Draws a phylogenetic tree for the genes in a column using a MUSCLE alignment and PhyML.
"rates" Button
Generates pairwise yn00 output of Ka, Ks and omega for all genes in a column.
S. cerevisiae gene boxes have an "i" information button than clicks through to the SGD title line description of the protein and its Gene Ontology terms. Rolling your mouse over a gene's box will also display any available information for that gene.
Every visualised MGOB page has a "+" button in its bottom left hand corner. Clicking the button displays the same MGOB data in a tabulated text format.
The control console has a "Flip" button to allow the user to swap the top and bottom tracks.
"Twist" Button
The control console has a "Twist" button to allow the user to invert the left-right sequence of the columns in the display.
Pkud_MGOB_CEN1
Pkud_MGOB_CEN2
Pkud_MGOB_CEN3
Pkud_MGOB_CEN4
Pkud_MGOB_CEN5
OPOL_MGOB_CEN1
OPOL_MGOB_CEN2
OPOL_MGOB_CEN3
OPOL_MGOB_CEN4
OPOL_MGOB_CEN5
OPOL_MGOB_CEN6
OPOL_MGOB_CEN7
Kcap_MGOB_CEN1
Kcap_MGOB_CEN2
Kcap_MGOB_CEN3
Kcap_MGOB_CEN4
Kcap_MGOB_CEN5
Kcap_MGOB_CEN6
Kcap_MGOB_CEN7
Kpha_MGOB_CEN1
Kpha_MGOB_CEN2
Kpha_MGOB_CEN3
Kpha_MGOB_CEN4
Scer_CEN1
Scer_CEN2
Scer_CEN3
Scer_CEN4
Scer_CEN5
Scer_CEN6
Scer_CEN7
Scer_CEN8
Scer_CEN9
Scer_CEN10
Scer_CEN11
Scer_CEN12
Scer_CEN13
Scer_CEN14
Scer_CEN15
Scer_CEN16
Anc_CEN1
Anc_CEN2
Anc_CEN3
Anc_CEN4
Anc_CEN5
Anc_CEN6
Anc_CEN7
Anc_CEN8
As well as understanding systematic names for S. cerevisiae genes (e.g. YAL063C), MGOB will also correctly identify SGD genetic names (e.g. FLO9 in the case of YAL063C) if inputted, as well as synonyms. In the former case it will bring you straight to the gene, in the latter case you will be asked to confirm the gene you are interested in. MGOB will also take as input the 'stem' of a SGD systematic name (e.g. YAL064) and present the list of genes with that stem (YAL064W-B, YAL064C-A, YAL064W in this example).
If you know the number of a pillar of interest (they are used mainly as internal IDs in MGOB but can be seen embedded in various links) and wish to navigate to it (without having to recall a gene in the pillar) then type in 'P' followed by a pipe character ('|') followed by the pillar number. MGOB will bring you to the pillar with the browser focused on a gene in it (a non-WGD gene if one is present). This is mainly a tool for curators. Pillar numbers may not remain the same from version to version.
 The Methylotroph Gene Order Browser (MGOB) reveals conserved synteny and ancestral centromere locations in the yeast family Pichiaceae
The Methylotroph Gene Order Browser (MGOB) reveals conserved synteny and ancestral centromere locations in the yeast family PichiaceaeDouglass AP, Byrne KP and Wolfe KH
FEMS Yeast Research. 2019 Sep;19(6):foz058
| Supplemental: | Information |
 The Yeast Gene Order Browser: combining curated homology and syntenic context reveals gene fate in polyploid species
The Yeast Gene Order Browser: combining curated homology and syntenic context reveals gene fate in polyploid speciesByrne KP and Wolfe KH
Genome Research. 2005 Oct;15(10):1456-61
| Supplemental: | Methods | Table 1 | Table 2 |
